Anatomy of Muscles
Muscle is a contractile tissue which brings about movements. Muscle can be regarded as motors of the body.
Types of Muscles
It has three types-
1- Straited/skeletal
2- Non-straited/smooth
3- Cardiac
1- Straited/Skeletal Muscle - it is present in the limbs, body wall, tongue, pharynx and beginning of oesophagus. They are long and cylindrical and fibres are unbranched and multinucleated. These are bounded by sarcolemma and bands present in light and dark . it is voluntary, very rapid contraction and blood supply is abundant and nerve supply from cranial nervous system.
2- Non-striated/Smooth - they are present in oesophagus, urogenital tract, urinary bladder , blood vessels, iris of eye, arrector pili muscle of hair. It looks like a spindle shaped, they are unbranched fibres and uninucleated .
They are bounded by plasmalemma and light and dark bands absent , nerve supply from autonomic nervous system and blood supply is scanty. They are involuntary and no intercalated discs.
3- Cardiac Muscle - it is present in wall of heart. It looks like a short and cylindrical and branched fibres ,uninucleated and bounded by plasmalemma.
In these muscle faint light and dark bands are present, intercalated disc present and a characterstic feature and nerve supply from autonomic nervous system, blood supply is abundant. Involuntary movement present in this muscle and rapid contraction.
Parts of Muscles - it has two ends and two parts -
A)- Two Ends
1-)Origin
2-)- Insertion
1-)- origin- it is one of the muscle which mostly remains fixed during its contraction.
2-)- Insertion- it is other end which mostly moves during its contraction. aIn the limb Muscles , the origin is usually proximal to insertion.
B-)- Two parts-
1-) Fleshy part
2-) Fibrous part
1-) Fleshy part- it is contractile, and is called the "belly " .
2-) Fibrous part- it is non-contractile and inelastic . when cord - like or rope like , it is called tendon .
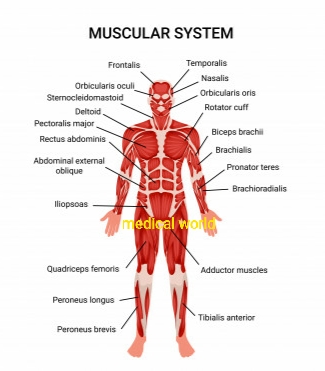
Naming the muscle of Chest,Skeletal ,blow the knee and back
Features used in naming Muscles
Following features are used for naming the muscles.
Shape
1. Deltoid ( triangular)
2. Quadratus ( quadrangular)
3. Rhomboid ( diamond shaped)
4. Teres ( round)- teres major
5. Gracilis (slender)- gracilis
6. Lumbrical(worm like)- lumbricals form
7. Rectus( straight) - rectus abdominal
Size
1. Major(big)- pectoralis major
2. Minor (small) - pectoralis minor
3. Longus(long)- adductor longus
4. Brevis( small) - abductor pollicis brevis
5. Latissimus(broadest)- latissimus dorsi
Number of heads
1. Biceps (two heads)- biceps brachii
2. Triceps (three heads)- triceps brachii
3. Quadriceps( four heads)- quadriceps femoris
Position
1.Anterior (front)- tibialis anterior
2.Posterior (back)- tibialis posterior
3. Lateralis (lateral side)- vastus lateralis
4. Medialis (medial side)- vastus medialis
5. Superior (upper side)- superior rectus of eyeball
6. Inferior (lower side)- inferior rectus of eyeball
Nerve supply of skeletal muscle-
The nerve supplying a muscle is called motor nerve. In fact it is a mixed nerve and consists of the following types of fibres.
These fibres are motor fibres and sensory fibres , so motor fibres are contain 60% and sensory fibres are contain 40%.
Nerve supply of smooth muscle -
According to nerve supply the smooth muscles are classified into -
Single - unit type : seen in intestine.
Multi-unit type: seen in the Muscles of the ductus deferens.
Nerve Supply of muscle -
Heart is supplied by sympathetic and Perasympathetic nerve fibres. Sympathetic nerves stimulate both the heart rate and blood pressure and dilate the coronary arteries. The sensory fibres convey painful impulses from heart.
Perasympathetic fibres decrease and normalise the heart rate their sensory fibres are involved with visceral reflexes.


0 Comments